
Archives
-

Tecnología, Justicia y Gobernanza: Retos Digitales en la Selección y Evaluación de Magistrados
Vol. 5 No. 1 (2025)En esta edición, Tecnohumanismo se adentra en el complejo y necesario diálogo entre la tecnología y el Derecho, explorando cómo las herramientas digitales están transformando los procesos judiciales y, en particular, los mecanismos de selección, evaluación y control de jueces y fiscales. A través de un enfoque multidisciplinario, abordamos el papel de la Junta Nacional de la Magistratura (JNM) en la era digital: desde la trazabilidad en los procesos de evaluación, el uso de inteligencia artificial para el análisis de expedientes, hasta los dilemas éticos de la automatización en decisiones de gobernanza judicial.
¿Qué implica una justicia verdaderamente digital? ¿Cómo garantizar la transparencia sin sacrificar la independencia del Poder Judicial? ¿Puede la tecnología fortalecer la meritocracia en instituciones como la JNM? Estas y otras preguntas estructuran los ejes temáticos del presente número.
-

Perspectivas Interdisciplinarias en Ingeniería, Tecnología y Ciencias Sociales
Vol. 4 No. 4 (2024)Este número de la Revista TecnoHumanismo aborda el enfoque y alcance interdisciplinario como eje central para la integración del conocimiento en los campos de la Ingeniería, Tecnología, Ciencias Sociales, Ciencias Médicas y Biotecnología. Contribuciones originales e inéditas, sometidas a rigurosos procesos de arbitraje, presentan reflexiones, investigaciones y revisiones que fortalecen el diálogo entre las ciencias y las humanidades.
El Vol. 4 Núm. 4 se consolida como un espacio para la exploración de ideas innovadoras que trascienden los límites disciplinarios, fomentando el desarrollo científico y el intercambio académico a nivel nacional e internacional. Este volumen destaca el compromiso de la revista con la diseminación de conocimiento interdisciplinario y su impacto en la sociedad contemporánea.
-

Innovaciones y Perspectivas en la Intersección de Tecnología y Humanismo
Vol. 4 No. 3 (2024)En el Volumen 4, Número 3 (2024) de la Revista TecnoHumanismo, presentamos un conjunto de investigaciones que abordan las últimas innovaciones y perspectivas en la convergencia de la tecnología y el humanismo. Esta edición, editada por el Centro de Investigación & Producción Científica IDEOs en Lima, Perú, reúne artículos científicos en español que destacan la relevancia de un enfoque interdisciplinario para abordar los desafíos contemporáneos.
En este número, los lectores encontrarán estudios que exploran desde la ética en la inteligencia artificial hasta las aplicaciones de la tecnología en la educación y la salud. Además, se incluyen análisis sobre el impacto social de las nuevas tecnologías y cómo estas pueden ser utilizadas para promover el desarrollo sostenible y mejorar la calidad de vida.
Dirigida a investigadores, académicos de grado y posgrado, y al público interesado en el pensamiento crítico y la evolución tecnológica, esta publicación busca promover el intercambio de ideas y el avance del conocimiento en un mundo en constante cambio. La revista TecnoHumanismo se compromete a ofrecer un espacio para la reflexión profunda y el debate informado, contribuyendo así al enriquecimiento del pensamiento interdisciplinario y al desarrollo de soluciones innovadoras a los problemas globales actuales.
-

Innovaciones en Ingeniería Sostenible para un Futuro Resiliente
Vol. 4 No. 2 (2024)El volumen 4, número 2 del año 2024 de la revista "Tecnohumanismo" se centra en la exploración de las intersecciones entre tecnología y humanismo en el siglo XXI. En esta era de avances tecnológicos rápidos y cambios sociales profundos, surge la necesidad de comprender cómo la tecnología puede ser moldeada y dirigida por valores humanísticos para promover el bienestar individual y colectivo. Este número especial presenta una amplia gama de investigaciones y reflexiones sobre temas como la ética en la inteligencia artificial, la equidad en la era digital, la relación entre la tecnología y la identidad humana, y la responsabilidad social de los ingenieros y científicos. A través de diversos enfoques interdisciplinarios, expertos en tecnología, ética, filosofía y ciencias sociales examinan cómo la tecnología puede ser utilizada para fortalecer la democracia, fomentar la inclusión y abordar los desafíos globales, al tiempo que se respetan los valores humanísticos fundamentales. Este número ofrece una plataforma para el diálogo y el debate sobre el papel de la tecnología en la construcción de un futuro más humano y equitativo.
-

Avances Científicos: Explorando el Futuro Tecnológico
Vol. 4 No. 1 (2024)Avances Científicos: Explorando el Futuro Tecnológico" es una cautivadora odisea a través del cosmos del conocimiento, donde la ciencia y la tecnología convergen para desvelar los secretos más profundos del universo. Esta obra maestra editorial lleva a los lectores a un viaje fascinante, adentrándolos en los rincones más innovadores de la investigación científica y las últimas fronteras tecnológicas.
Desde las maravillas de la inteligencia artificial hasta las proezas de la ingeniería genética, cada página de esta publicación ofrece una visión única y esclarecedora de los desarrollos más recientes que están dando forma al mañana. A través de narrativas apasionantes y análisis profundos, "Avances Científicos" revela cómo la fusión de ciencia y tecnología está transformando radicalmente nuestra comprensión del mundo y redefiniendo los límites de lo posible.
Sumérgete en un torrente de descubrimientos emocionantes, donde las mentes más brillantes del mundo desafían constantemente las convenciones y exploran nuevos territorios de conocimiento. Desde los laboratorios de investigación hasta los proyectos más vanguardistas, esta obra invita a los lectores a vislumbrar el futuro a medida que se despliega ante nosotros, lleno de promesas y oportunidades emocionantes.
-

Revolutionizing Energy: Integration of Artificial Intelligence in Electrical Grids
Vol. 3 No. 4 (2023)In the very fabric of our energy infrastructure, a silent yet powerful revolution is taking shape: the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into our Electrical Grids. In this exciting intersection of technology and engineering, we are witnessing a transformation that redefines not only how we generate and distribute energy but also the pivotal role that AI plays in this equation.
The traditional narrative of electrical grids is being rewritten with intelligent algorithms that anticipate, adapt, and optimize in real-time. This fusion of technologies not only enhances efficiency but also ushers in a new era of resilience and sustainability in our energy landscape.
TecnoHumanism celebrates this revolution, where artificial intelligence becomes the indispensable ally in addressing increasingly complex energy challenges. Through this integration, we are not just revolutionizing energy but also solidifying a vision of the future where technology and humanity converge to create a smarter and more sustainable tomorrow.
-

Science in relation to ethics
Vol. 3 No. 3 (2023)Ethics transcends everything we do, so it undoubtedly also affects how we do science. We understand by science the work of discovering how the universe works, what its operating laws are, how we can model them, and ultimately how we can better foresee the future. Advances in science allow us to make better use of natural resources through the new technologies to which it gives rise. Technology is the practical consequence of science. Technology marks how we can live in its practical aspects (which is modulated by the reality of the economy); and science marks how we understand the world and our position in it (in contrast and constant dialogue with philosophy and religion). And in both cases, science and technology, we have to see how they coexist and how they interact with ethics.
We are going to focus here on a couple of dimensions of this “science + ethics” pairing: 1) how we apply the results of science through technology and how ethics affects it, and 2) how science is done, how it develops and how ethics affects this process.
It is a commonplace to say that science is "neither good nor bad" since what it is is the verification of our mental model of the universe. Some basic principles and some mathematical hypotheses of the model are ventured, its projections are calculated in practical situations and said quantities are measured in reality. If they agree and are repeatable, we are convinced that the model is adequate, that is, it adequately reflects reality in the measured circumstances. Over time, these models cover more and more areas of reality, from the simplest to the most complex, from the most basic components of matter to the astronomical universe, from inert materials to living bodies, from the basic structure of life to the entire changing environment of the individual and his society - and with increasing precision. It really is an exciting activity.
But knowing is power. And the ethics of each one is the one that will dictate the way in which said knowledge and the corresponding technologies are applied. Computers, communications and the internet have made our lives so much easier, giving us access to much more information much faster and cheaper – but they can also be used to carry out destructive attacks on privacy, against financial institutions, and in a world of the “internet of things”, against physical infrastructures, etc. That is why we have to equip ourselves with rules of coexistence, with laws that reflect the appropriate balance between the freedom to use technology with the necessary protection of people and institutions that we have given ourselves.
This balance takes different forms depending on the social environment in which it develops, and therefore the prevailing ethics. Finding and agreeing on such balances becomes more difficult the faster the evolution of technology, and therefore the status quo, than what is economically feasible for the majority of society. A clear case is the technological explosion to this day of information technology and the Internet. At the base of this explosion is the discovery of semiconductors and materials science. This revolution has collapsed many of the productive and economic models of a few decades ago, while it has opened up endless new opportunities. Information is available to everyone – or almost everyone. The situations raised by the defense of the copyright of digitizable products (such as literature, music, video and cinema), by the impact of Wikileaks and, recently, by the NSA wiretaps demonstrate at the same time how easy which is having access to much/all information, such as the complexity of resolving the dilemma of where is the balance point that we all consider most appropriate, fairest. And you have to decide very quickly, since technology advances rapidly. Our problem is that the institutions are not capable of digesting this speed of change, and this causes clear dysfunctions. But it is clear that a fundamental guide to do so is to have some basic and widely accepted ethical principles. This in turn depends on an adequate education in ethical values. Society needs to agree on which are the priorities, how to transfer them to the new generations and how to adapt them based on new horizons of knowledge.
-

3D printing for the manufacture of prostheses
Vol. 3 No. 2 (2023)3D printing is changing the way dentures are made. This technology has made the design and production of prosthetics incredibly affordable for those without limbs. In the United States, prosthetics can be very expensive, approximately $5,000 to $50,000, resulting in a significant financial burden for individuals who need to purchase one. In addition, the prostheses must be tailored to each individual, which requires a production time of the order of weeks or months, which can become extremely tedious.
3D printers give anyone the ability to design and print custom parts in great detail, which has made prosthetics more accessible to individuals around the world.
Next, the types of prostheses that are most frequently created with 3D equipment will be mentioned, and a brief mention will be made of the companies that are dedicated to their production.
As can be seen, 3D printing in the world of prosthetics has been used efficiently and innovatively. Therefore, it is clear that research and development of projects involving 3D equipment in the field of medicine should continue to be encouraged. Over the years, the discoveries and processes related to 3D printing will be incredible, and they can save a lot of work, time and money.
Maria Gabriela Garcia
-

Patrimonial, Business Civil Law and Corporate Social Responsibility using technology
Vol. 3 No. 1 (2023)When talking about Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), one usually thinks of companies that produce tangible goods whose production activities cause a visible or measurable impact to a greater or lesser extent.
It is worth asking what happens in the case of companies that produce intangible goods, particularly information technology (IT), where the impact is neither visible nor measurable in such an obvious way, but it is nonetheless irrelevant. since the actions of such companies affect -whether directly or indirectly- a large part of the economic and cultural aspects of society.
The concept that companies have responsibilities that extend beyond their shareholders is as old as the shareholders themselves. In the 19th century, many companies built special housing for their employees, believing that an employee living well would be more productive than one living in precarious conditions.
Since its inception, companies have had an economic contract with the companies in which they acted. Said contract assigned the former the function of producing goods and services efficiently, generating and maintaining jobs, obtaining profits (part of which were reinvested in the production process) and complying with the tax charges and contributions that allowed them to maintain these companies.
Classical economic thought maintains that in a market with ideal operating conditions, compliance with the economic contract by companies would allow a general welfare state to be achieved. But since these ideal conditions are not verified in practice, the functioning of the markets is not carried out efficiently and market failures occur. This is due, in large part, to the fact that the economic system ignores all those phenomena that are not expressed through a monetary exchange. These phenomena produced by companies and that affect those who are not part of them, are known as "externalities".
At first glance, it could be assumed that there are no links between CSR and computing activity, since they are apparently dissimilar disciplines. However, and as has been exposed, there are numerous points of contact between both disciplines. Computer science has a historical and philosophical basis based on principles of collaboration, transparency (free access to information) and contributions to society and, although these principles are not inherent to the activity (that is, it can be carried out even without apply these principles), knowledge of them constitutes a solid foundation to apply in the definition of CSR policies and programs in ETIs.
In our country, CSR is a discipline of recent appearance, particularly in medium-sized companies. Due to this, and added to the fact that the activity of the ETIs does not produce visible impacts, the challenge of generating awareness is presented here so that CSR practices become one more part of the actions of the ETIs. .
In order to carry out this challenge, the participation of all interested parties (stakeholders) is necessary, in such a way that the actions related to CSR cover the widest possible spectrum. However, this will not be possible if CSR is considered as a corporate fashion lacking real and deep support, and whose sole purpose is to improve the image of the company in order to increase sales. It is in this aspect that a change of vision must take place that extends to the entire company, originating from the management and expanding from there to all sectors.
It is the wish of the person who writes this that the mentioned challenge can materialize in the coming years.
Maria Gabriela Zuleta
-

New educational technologies 2023
Vol. 2 No. 4 (2022)As a result of the recent pandemic, it has become clear the need to educate young people and children with accessible content from home, in digital environments in addition to giving the student a leading role in the teaching-learning process.
Thus, in the XXI century two major educational trends are identified, the first one that focuses more on the use of technology and digital platforms to impact the teaching-learning process, leaving aside the curriculum and teacher intervention, and the second one, which puts in the center the personalization of student learning, integrating the teacher, the curriculum and the context within the process.
However, pedagogical models continue to change and transform themselves to improve for the benefit of those involved such as students, teachers and even parents. It is worth mentioning that, among the educational trends, the collaborative classroom modality is gaining weight. Its purpose is for students to be more proactive, that is, to participate in class and share their knowledge and experiences with their classmates.
Teacher-student communication would no longer go in only one direction, but the bidirectionality of the interaction would be the key that would mark these relationships. Thus, collaborative learning would be directed by the students themselves, relegating the teacher to a kind of referee or moderator, similar to inverted learning.
Likewise, the issue intends to investigate and delve into other related issues such as formative assessment, language and cultural barriers, assessment tools, digital competencies, research skills, pedagogical support, sustained attention, public policies for the education sector and, of course, the boom that virtual educational environments are having.
Maria Gabriela Zuleta
-

Violence against women and other urgent problems to be resolved
Vol. 2 No. 3 (2022)The United Nations defines violence against women as "any act of gender-based violence that results in, or is likely to result in, physical, sexual or psychological harm to women, including threats of such acts, coercion or arbitrary deprivation of liberty, whether occurring in public or in private life".
Intimate partner violence refers to intimate partner or ex-partner behaviors that cause physical, sexual or psychological harm, including physical aggression, sexual coercion, psychological abuse and controlling behaviors.
Sexual violence is "any sexual act, attempt to consummate a sexual act or other act directed against a person's sexuality through coercion by another person, regardless of their relationship to the victim, in any setting.
In Peru, the Ministry of Health (MINSA) through the National Center for Epidemiology, Prevention and Disease Control (CDC Peru) reported more than 17 thousand cases of violence against women during 2022. The entity reported that, from January to October 2022, cases of violence against women within the group of family violence, accounted for 86% of total notifications nationwide.
Thus, this is a daily and highly prevalent problem in our society, as well as serious and urgent to solve. Official reports indicate that 7 out of 10 adult Peruvian women have been victims of psychological, physical and/or sexual violence at some point in their lives and, after the confinement motivated by COVID-19, this situation has worsened.
For this reason, it is important to study this problem in greater depth and this issue explores resilience in women who have been victims of violence, teenage pregnancy and other socially relevant topics.
María Gabriela García
-

New technologies applied to a post-pandemic context and their repercussions in the various social sectors
Vol. 2 No. 2 (2022)2021 has been described as "the great year of the technological leap" due to the expectation generated in terms of developments in Artificial Intelligence, Big Data, Internet, Broadband, security and digital banking amid the effects that the pandemic has left ; Therefore, it is important to keep in mind the study of the technological trends that are coming for the next year, having a firm ground to know which areas must be strengthened and become part of the global digital transformation and the new normality.
The world is changing at a speed never seen before due to the situations that were generated as a result of COVID-19, a disease that triggered a pandemic that no one was prepared to face. And, in the midst of uncertainty, technology has been the lifeline for many businesses and organizations that thought of this element as a luxury and not as a basic necessity.
Thus, this edition delves into the impact of these technologies in a post-pandemic context and their links with problems such as the continuity of business operations, especially SMEs and micro and small businesses in the sectors, commerce, industry and services.
Also other issues such as misinformation, to the extent that the SARS CoV-2 pandemic caused the search and dissemination of health information, which spread on the internet as it is a great source of information, even when the data was not regulated and its veracity remains questionable. The greatest risk is that the information found on the Internet can influence users; however, it often lacks scientific support, a circumstance that causes concern for scientific societies, governments, and users.
Also on education, since in the country the pandemic caused the suspension of face-to-face teaching, for which alternatives were sought to continue the teaching-educational process even in conditions of restrictions, social isolation, among other inconveniences. The life of university students in the same way changed radically, making their study relevant.
Likewise, about creativity, understood as that capacity that throughout the history of the human being has allowed it to grow, develop, in general, progress in an innovative and efficient way, even in moments of great difficulty where individuals have been forced to deal with natural phenomena, disasters, etc. For this reason, it was worth reflecting on the effects that the complex moment that we are currently experiencing has had on artistic creativity, characterized mainly by the Covid-19 pandemic and being able to understand how it has served to deal with it. Finally, on metacognitive development, ICT videogames, among other relevant aspects.
It is crucial to investigate and explore the various paths in which new technologies are presented, above all, as mentioned, in a changing and increasingly demanding environment. And, in which they adopt very different roles and in sectors that are unlikely and others that are very obvious. It is worth mentioning that only through study and knowledge will it be possible to have clarity about the kind of resources that are currently available in the world and the benefits that they represent.
Maria Gabriela Garcia
-

Challenges in a post-millennial context: environmental, educational, scientific and business problems in the 2000s
Vol. 2 No. 1 (2022)The end of the reign of millennial youth is nearing –soon they will be part of prehistory– to make way for generation Z (those born between 1994 and 2010). As expected, there are already a multitude of labels and descriptions that try to offer a profile of this heterogeneous group of young people up to 24 years of age who, already born in the midst of the digital age, cannot conceive of the world without the Internet.
Thus, the Internet is like a wave, for which society is not fully prepared. In this line, a series of changes and modifications in society must be conceived as a response to the technological environment and adapt to the new generations, who demand more and new things.
It should be noted that among the main characteristics that are separated from millennial posts is the marked tendency to be pessimistic, anxious, to avoid risks and not have great aspirations. And, since their main source of information is social networks, their knowledge and understanding of current affairs could be superficial – due to fake news. Likewise, for millennials, there is no life without the Internet: at the time it was the desktop computer, then the notebook and currently the Smartphone, but the people we are talking about cannot conceive of their relationship with the world without these devices and most of them of what they do (from watching movies to working or meeting people or buying products) will always be using the latest technology.
As a consequence of this, researchers and current literature increasingly seek to understand this profile and study the links it has with other aspects of society; Among a diversity of topics, this issue analyzes reading comprehension in university students of the aforementioned generation, especially knowing that a central characteristic of this generation is the extensive and daily use that they make of currently available technological tools. This particularity gives them a different lifestyle from other generations and impacts their reading habits: they prefer the screen to printed text.
For this reason, educational paradigms must consider the use of social media and other technological environments for learning and incorporating tools considered by some as negative cultural patterns for learning and turning them into new scenarios for the exchange of information, knowledge and interaction between the actors of the educational process. Above all, to the extent that the literature indicates that making reading interesting improves interest in reading, develops basic skills for reading comprehension and therefore improves academic performance.
Also studies of their creativity and imagination, the latter analyzed from the studies of Kant, who distinguishes imagination as reproductive and productive. Both have a synthetic and representative-intuitive aspect, except that the first (reproductive imagination) has its place in psychology and the second (productive imagination) in transcendental philosophy and seeks to delve into its theoretical and philosophical aspects. In addition to the organization and planning in consciousness.
Maria Gabriela Garcia
-

Covid 19 and its repercussions on society at an economic, legal, technological and educational level
Vol. 1 No. 4 (2021)Since it first emerged in late 2019, the new virus, SARS-CoV-2, has had a number of impacts on the people it infects. Some become severe from COVID-19, the disease caused by the virus, and require hospitalization, while others have mild symptoms or are even asymptomatic.
There are several factors that influence a person's susceptibility to having a severe reaction, such as their age and the existence of other medical conditions. But a person's genetics also play a role. For this reason, it is important to investigate further into the forms that this disease took and how it impacted not only on health but also on other sectors of society.
For example, in the country, it should be remembered that the SARS-COV-2 virus, which causes COVID-19, was officially reported on March 6, 2020, and on the 25th of the same month, Supreme Decree No. 094- 2020-PCM, which established "the social isolation measures aimed at a new social coexistence and the State of National Emergency was extended due to the serious circumstances that affect the life of the Nation as a result of COVID-19."
These measures brought to light, not only the serious deficiencies of the health system, but also what should be the role of the industry and society in dealing with the pandemic as a result of the lack of response capacity of health establishments, in reference to human resources (health professionals) and material resources (medical equipment and infrastructure).
Thus, it posed great challenges for the education sector. Three fields of action were generated: the deployment of distance learning modalities, with a diversity of formats and platforms (with or without the use of technology); the support and mobilization of staff and educational communities, and attention to the health and comprehensive well-being of students. However, the government's efforts were not enough since around 124,533 students interrupted their studies in the educational system nationwide due to the aforementioned factors.
Meanwhile, in the Peruvian economy a pronounced drop in formal employment was observed in 2020 (the first months of confinement). However, since July of that year, formal employment gradually recovered until it registered positive growth rates towards the end of the same year. It should be noted that the economy has not only been affected by the pandemic, since globalization and constant social variations have historically led to negative repercussions, affecting the well-being of society in general.
Likewise, other issues such as accounting and financial analysis, business competitiveness, taxes, working capital, operational management, among other relevant issues for today, are linked in this issue.
Maria Gabriela Garcia
-

Blockchain and the challenge of technological resources to support education, management, accounting and public service
Vol. 1 No. 3 (2021)The United Nations defines violence against women as “any act of gender-based violence that results in, or is likely to result in, physical, sexual or psychological harm to a woman, including threats of such acts, coercion or arbitrary deprivation of freedom, whether they occur in public or private life.
Intimate partner violence refers to behaviors by a partner or ex-partner that cause physical, sexual, or psychological harm, including physical assault, sexual coercion, psychological abuse, and controlling behaviors.
Sexual violence is “any sexual act, attempted sexual act, or other act directed against a person's sexuality through coercion by another person, regardless of their relationship to the victim, in any setting.
In Peru, the Ministry of Health (MINSA) through the National Center for Epidemiology, Prevention and Disease Control (CDC Peru) reported more than 17,000 cases of violence against women during 2022. The entity reported that, in January As of October 2022, cases of violence against women within the group of family violence represented 86% of the total notifications at the national level.
Thus, this is a daily and highly prevalent problem in our society, as well as a serious and urgent problem to be resolved. Official reports indicate that 7 out of 10 adult Peruvians have been the victim of psychological, physical and/or sexual violence at some point in their lives and, after the confinement motivated by COVID-19, this situation has worsened.
For this reason, it is transcendental to study this problem in more depth and in this issue, in this regard, resilience in violated women is explored. Also about adolescent pregnancy, our country being the place where 13 out of every 100 female adolescents are already mothers or are pregnant. This indicator – which is alarming – is even more so when we focus on the Amazon regions, where we can find up to 40 out of 100 adolescents who are already mothers or are pregnant.
Even worse, the adolescent and young population of the country and the region face development challenges, aggravated and deepened by the effects of COVID-19. These effects have exacerbated gender violence, gaps in access to health, and the burden and job opportunities, especially for women. Faced with this, two of the main situations that limit the freedom of decision of girls and young people are: pregnancy and adolescent maternity. Both are cause and consequence of the violation of their rights, constituting barriers to their present and future development, and that of their families.
This problem does not remain in the theory or in the social, but also transcends the educational. It is worth emphasizing, then, the urgency of taking action in the Government to incorporate and improve the contents of comprehensive sexual education in Peruvian schools. It was previously reported that the Executive Branch was determined to implement information in schools that promotes equality, appreciation and respect for one's own body and that of others, self-esteem and a critical sense so that boys and girls can respond to the various situations they face and which are typical of their age.
Maria Gabriela Garcia
-

Food and technology: the new links between health, science, education and innovation
Vol. 1 No. 2 (2021)Peru offers the world a great diversity of products that are characterized by having important nutritional attributes. Currently, thanks to Peruvian gastronomy, which is increasingly positioned internationally, Peruvian superfoods have also been staged.
Peruvian products such as fruits, grains, vegetables, roots, herbs and fish have become a global food trend thanks to the properties and health benefits they offer. Superfoods receive this name because they are "functional foods that not only provide vitamins and minerals, but also have some of them in great excess and, therefore, help health and provide benefits."
This issue will address the benefits of superfoods, especially when taking as a context a changing environment in terms of food as well as health and technology, in such a way that not only is there the rise of the superfood concept, but also other that enter into a coalition such as food insecurity, contributing to the understanding of the meanings that are linked to this concept, specifically regarding: risks in the habitual diet of low-income families; long-term changes in your diet and context; as well as their efforts to protect and even improve family nutrition.
Nursing care will also be addressed, knowing that health institutions worldwide recognize the challenges that the arrival of a globalizing world entails, assuming the responsibility that quality has in the continuous improvement of care. The perspective from which the maximum well-being and safety of the patient can be assessed is through the appreciation that the patient has of the care he receives during his hospital stay, care that translates into client/patient satisfaction or dissatisfaction.
Also about new technologies in Peru, especially since technological development is still one of the main weaknesses in the country, despite the progress made in recent years. For example, it is worth mentioning innovative currents that are being presented in the country and that are worth studying in depth, such as those mentioned below.
First, emotional intelligence, a concept defined by Mayer as “an ability to perceive, assimilate, understand and regulate one's own emotions and those of others, promoting emotional and intellectual growth. In this way, this information can be used to guide our way of thinking and our behavior”. Linked to this, emotional education, which refers to the continuous and permanent educational process, which aims to promote the development of emotional skills as an essential element of human development, in order to train them for life and with the aim of increasing personal well-being. And social.
Likewise, the teaching-learning methods that are gaining strength in the community, learning styles, pedagogical leadership, research platforms among other problems that are intertwined with its operation and the support in technological and innovation resources as can be seen in each one of them.
Maria Gabriela Garcia
-
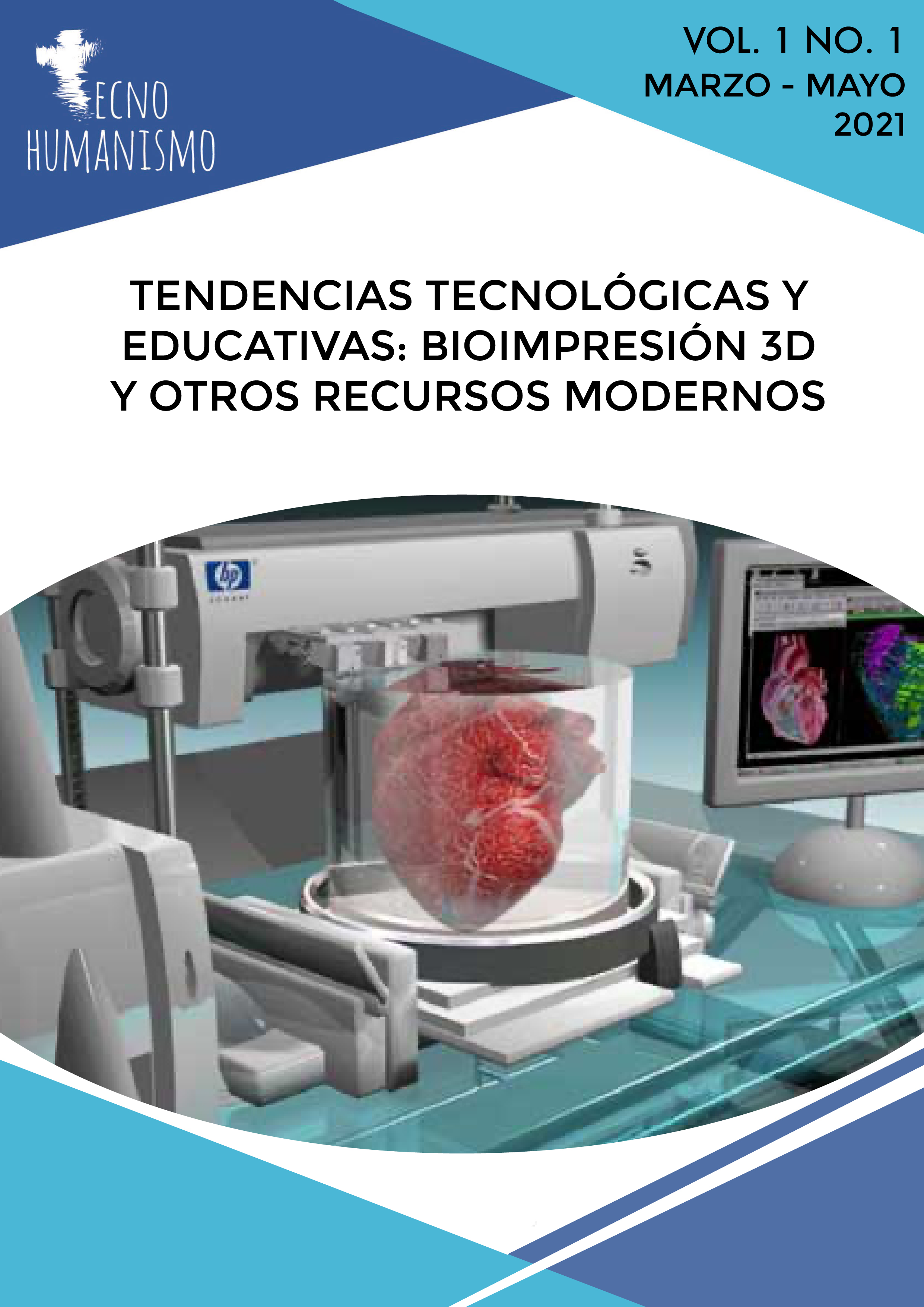
Technological and educational trends: 3D bioprinting and other modern resources
Vol. 1 No. 1 (2021)Currently, the technology and resources that have emerged (and continue to emerge) become an element of change and improvement in the life of the human being. It should be noted that, thanks to innovations, people have been able to achieve positive development in key sectors such as health and education. For this reason, it should be noted that technology has contributed incalculable benefits to humanity, which is particularly noticeable today, when the world was forced to face phenomena such as the COVID-19 pandemic.
Thus, for example, this issue addresses the relevance of tools such as the 3D bioprinter, which is a technological evolution of conventional 3D printers since it builds biological structures with a material called "bioinks", which are made from cells. mothers. With bioprinting, it is possible, through a layer addition system, to produce biological materials such as skin, tissues and even organs (kidneys, hearts and livers). Likewise, one of the main advantages is the use of the patient's cells to carry out the entire process. Thanks to these cells, tissues and organs customized to the needs of each patient can be printed, although it has not yet been able to assess whether the body will accept it or not.
It is worth noting the great technological innovations that are associated with the use of the cloud. This is another key element that has been gaining strength since 2010, when this new computer and technological architecture was consolidated, reaching users who currently use its services in various aspects of human life. Likewise, both large companies and small and medium-sized companies are progressively migrating to the cloud. For all these reasons, it is pertinent to address the forms and uses that have been attributed to this service and the ways in which it is involved in business, education, social life, among others.
Along with technological innovations in different areas of society, since technology is also created and expressed in reason and in clear articulation with the human condition. Therefore, education has not been left behind, since over the years both worlds have been mixed to create tools and digital environments in which the potential of human beings can be better developed and the way in which they approach to knowledge. The knowledge society is a society of exchange of technology, information, development and education.
Along these lines, Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) have reached educational classrooms at great speed and today demand to be used in all its forms. The digital era has changed pedagogical models, making teachers change work methodologies and use technologies to improve educational processes with innovative resources.
Thus, you can see in this article some articles related to learning strategies, the development of critical thinking, collaborative learning, and the quality of training in times of pandemic.
The objective in this issue involves emphasizing the forms that technology has been adopting at the same time that it has become more vigorously involved in other sectors such as health and education and the benefits that this entails on the roads, even when they are unlikely.
Maria Gabriela Garcia















